
Most companies revolve around one common goal: to provide value to their customers. From ideation to project management, everyone is invested in building a product that everyone will love. With so many ideas and features, it can be challenging to choose the right one. Some may align with your brand, while others offer long-term usability; at this point, you have no idea where to start.
This is where the kano model comes in. The ultimate asset to building long-term value products that can guide your company to the next economic boom. Here’s all you need to know about the Kano model, from categories to how the process works.
What is the Kano Model?
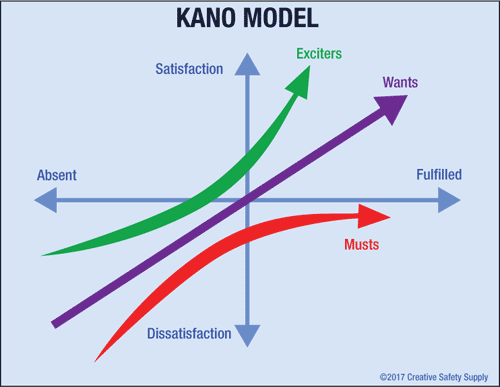
The Kano Model, pronounced as “Kah-no,” is an analysis tool to help companies build a product that’s most likely to satisfy customers. From ideation to launch, companies have to choose between features and determine whether or not to add them based on their overall cost, usability, and complexity. This approach helps design products that have a high rate of satisfaction.
Whether you are exploring market trends or about to market a new product, the Kano model can be an asset you can use to make strategically sound decisions in the long run.
Categories Of The Kano Model
The Kano Model works by breaking the features of products down into groups based on how they contribute to customer satisfaction. There are five categories identified. A product or feature can be listed in any one of the categories. The category that it is in, however, can change over time based on changing attitudes of consumers.
Each category is named after a translation from the original Japanese names written by Kano himself. The following image shows how the information and the categories can be tracked to make it easier for those using this model:
Must-Be Quality
Any product or feature that is in the must-be quality category is based on the requirements of the consumers. This is not to say that customers 'really want' them, but rather that they take them for granted. While it might seem that products in this category would be great marketing points, that is not typically the case. When a must-be quality feature is done properly, consumers won't really notice it. When they are done incorrectly, customers will be extremely upset.
An example of this would be the door on a vehicle. Customers want the door to open and close easily, lock and unlock conveniently and have windows that go up and down without trouble. This is just an expected feature of every vehicle, and customers don't put much thought into it at all. If a car was made with a door that didn't work, however, customers would not purchase that car.
One-Dimensional Quality
A one-dimensional quality product or feature is one that, when delivered properly, will ensure customer fulfillment. If it fails to deliver, customers will be dissatisfied. These items are typically used as part of marketing and talked up to boost sales.
An easy example of this is when a product advertises saying, 'contains 10% more than the competitors.' If the container does indeed contain 10% more, customers will be happy about getting a good deal. If the container actually only contains 5% more, customers will be upset because they were lied to.
In the example, the numbers would be real, but this can also apply to a perceived failure to meet the promise. If a company says 10% more by volume, a customer may weigh the product and find that they aren't getting 10% more than the competitor, even though by volume, there is 10% more. This is why it can be so important to look at consumer perception, not just raw numbers.
Attractive Quality
An attractive quality is one that will cause increased satisfaction to customers when done but won't cause dissatisfaction when the feature is missing. In most cases, these features won't be something that is explicitly advertised but rather a 'pleasant surprise' when the customer finds it on their own. This could be something like a coupon for their next purchase printed inside the box.
In many industries, the features that are listed under this category are what are most often used to set a product apart from the competition. When a base version of a product is similar no matter what company makes it, it is these attractive qualities that can help to swing a customer to one brand over another.
Focusing on attractive quality features is also smart because, in the event that the feature is not implemented properly, customers still won't be upset about having it there. This helps to limit the potential downside (other than the expenses associated with it) and maximizes the upside potential. Each industry will have to determine if this is a good strategy for their particular situation.
Indifferent Quality
An indifferent quality is something that customers won't care about one way or the other. In most cases, they aren't even aware of these types of features. In a cereal box, for example, an indifferent quality would be the thickness of the cardboard that is used. As long as the box holds the cereal, they don't care how thick it is. Manufacturers need to make this decision based on factors like cost, shipping durability, and more while keeping in mind that the end consumers won't ever give it a second thought.
Reverse Quality
Reverse quality features can cause consumer dissatisfaction, even when done properly. This is typical because not all customers are alike, and each group possesses a different set of likes and dislikes.
Knowing your target audience is an essential part of building a long-lasting campaign strategy. A good example of this is smartphones. Adding advanced technology to phones takes a lot of investment. The execution requires a major part of understanding in which you have to please a large portion of the market, despite the complexities that advanced technologies bring.
Advantages (and Disadvantages) Of The Kano Model
Advantage:
Safe Execution:
Using the Kano Model allows a company to take information from consumers and apply it directly to the planning and creation of products.
Save Time & Money:
Companies can conduct consumer surveys and use the information that is put into this model to evaluate whether a particular product or feature is worth the time and capital that it would take to create and produce.
Ensure Customer Satisfaction:
Results from surveys can be used to develop products or features that customers are more likely to want to purchase since a company will have a better idea of what types of things they demand.
Disadvantage:
Time-Consuming:
The model requires extensive research to analyze and assess patterns, which can take time to gather.
Mainly Based On Quantitative Data:
Research and findings are based on questionnaires or surveys that provide quantitative data (numerical results), which fail to provide any theory or backing. This will ultimately lead to more time invested in figuring out the “why” behind certain decisions.
Research Is Limited:
The data gathered can be interpreted by certain individuals who are aware of the backing and subject of the research. Results will need to be analyzed by other associating departments.
Outdated Techniques:
The Kano model is subjected to manual methods that focus on providing surveys or questionnaires, and as a result, they can take time to distribute and analyze.
Implementing the Kano Model to Your Business
Implementing the Kano Method is an easy process that will primarily be focused on gathering information, and training employees to use it properly.
In most cases, only specific employees will need to be given the education required to properly use this method, which can help to streamline the implementation of the Kano Method into practice. Execution of the Kano model requires keeping two essential factors, including:
Customer Satisfaction
One important thing to keep in mind when implementing the Kano Model is that, in the end, customer satisfaction is going to be the main measuring stick. This system can also help to eliminate waste and improve efficiency by only putting effort into things that customers want.
Customer satisfaction is a primary aspect however, cost, flexibility, and efficiency are also key factors to consider when determining high-value features of a product.
Using The Kano Model with Other Techniques
When implementing the Kano Model in a facility, other company strategies should be looked at to see how Kano and the others can complement each other. Given the fact that the Kano Model can help eliminate waste by identifying features or services that don't add value to the customer, it can be an important part of 5S strategies taking place within the facility.
It can also be implemented alongside lean strategies in manufacturing, medical, office, or other environments. These are very complementary strategies that can benefit from being in place and used to accomplish waste elimination, and improved customer satisfaction.
Additional Information on the Kano Model
Kano Model Template:
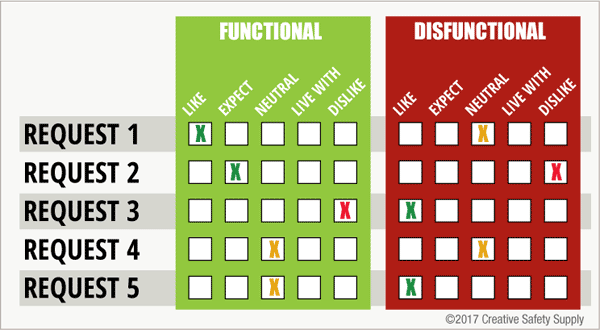
There are many Kano Model templates out there for completing different tasks more effective. Using a template for a Kano Survey will help ensure all the necessary questions are asked in the proper way, and that the information gathered is able to be properly used.
Using a template to track customer requests can also help to keep information in a more understandable format. This image shows how customer requests can be classified using the categories from the Kano Model.
Kano Model in Action
One of the easiest ways to understand how the Kano Model works in practice is to look at some real life examples. These examples show how certain things start off in one category of the model, and can move to other areas over time.
A great example of this is the cell phone battery. When smart phones first came out, they had batteries that didn't last too long, and were often quite bulky. People accepted this because the technology was new and the smart phones were performing things that many people never dreamed they could.
When slim form batteries came out that lasted far longer than older options, most people weren't willing to pay the added expense. In most situations, this feature was not implemented because the number of customers demanding it was insufficient. Over time, as price dropped and technology improved, a slim battery that lasted a long time moved from a 'attractive quality' to 'must-be quality.'
Other types of things will start off, and remain, in the same category indefinitely. Businesses need to be able to follow features and products closely so they always know how they fit into the Kano Model. Consistently gathering information from customers, and using it to evaluate how to change or improve products in order to maximize customer satisfaction and return on investment.
Design Products That Delight Customers With Creative Safety Supply
Consumer emotions influence market trends and decisions that companies make. It’s essential for companies to utilize strategic tools like the Kano model to market ideas and products that ensure economic growth. Plan your next product launch with Creative Safety Supply, the ultimate hub of business growth and management resources.
Resources
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kano_model
- https://www.qualtrics.com/au/experience-management/research/kano-analysis/
Similar Articles
- Continuous Improvement (A Kaizen Model)
- The Five Whys (Root Cause Analysis)
- Understanding the SIPOC Diagram in Six Sigma
- Bottleneck Analysis
- Fault Tree Analysis
- 5 Lean Principles for Process Improvement
- Job Safety Analysis
- Value-Added vs. Non-Value-Added Activities
- Value Stream Mapping (VSM Analysis)
- Process Cycle Efficiency (PCE)

