Effective workplace labeling improves safety and efficiency by clearly communicating potential hazards and guiding workers. When combined with the appropriate tools, like a thermal printer for creating durable labels, the work environment becomes safer and more productive.
Thermal printers expand beyond just label printing and are now widely adopted across various commercial sectors. Their speed, efficiency, and reliability have made them a popular choice for applications like receipt printing, barcode generation, and even specialized uses in healthcare and manufacturing.
In this article, we will explore the world of thermal printers and look at their working principles and applications across industries, helping you choose the right option for your facility.
How Does a Thermal Printer Work?
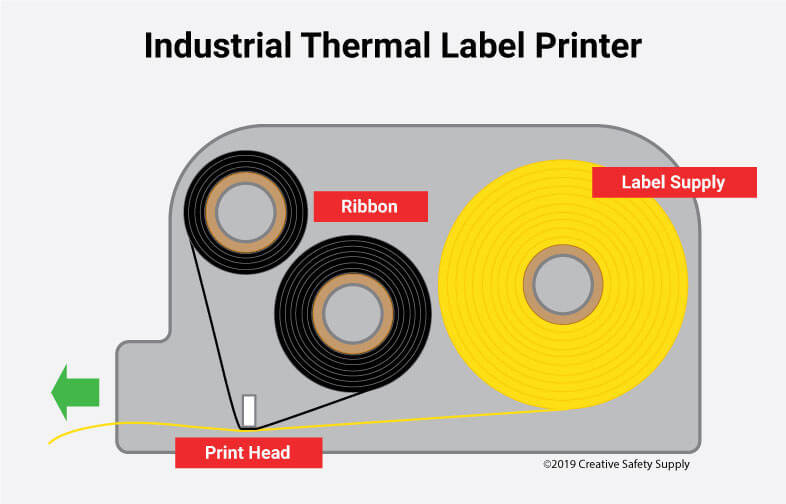
Thermal printers are a type of printer that does not use ink or toner to create an image. Instead, they utilize a heated printhead to create text and images by applying heat to a special type of paper or transferring ink from a ribbon onto a substrate. Depending on how they create an image, thermal printers are broadly categorized into two main types: direct thermal printers and thermal transfer printers. Let’s look at each type and its working principle.
Thermal Transfer Printer
A thermal transfer printer is a type of thermal printer that uses a heated print head to transfer ink from a ribbon onto a substrate, like a label or paper, to create an image or text. When printing, the printhead heats up in specific patterns, corresponding to the desired image. The heat from the printhead then melts the ink from the ribbon and transfers it onto the substrate, creating a durable image or text.
Thermal printers are ideal for environments that require printing a variety of things, since thermal printing can print effectively on a larger array of media than direct thermal models, including paper, polyester, and polypropylene materials. Thermal transfer printers are able to print pipe marking labels, wall signs, tickets, tags—just about anything. However, when changing from one material to another, the targeted material and ribbon must be compatible. This will ensure perfect performance.
The accurate media-ribbon combination can enable users to create high-quality labels that withstand environmental extremes, sun damage, chemical and water exposure, etc.
Typical uses for thermal printers utilizing the thermal transfer method include:
- Pipe marking
- Inventory identification
- Instrument identification
- Instructive labels
- OSHA-compliant notifications
- Safety warnings
- Certification labels
Beyond these core uses, thermal transfer printers are also utilized for retail price tags, product labels, barcode labels, and various other applications where durability and long-term readability are essential.
Direct Thermal Printer
Direct thermal printers use chemically treated, heat-sensitive media that darkens when applied to a thermal printhead. Unlike thermal transfer printers, this kind of industrial printer has no ribbon, ink, or toner. Because these don't require many components, direct thermal printers make for easy usage. Because there are fewer parts, they're more durable and tougher than inkjet printers. Most mobile printers—the kind that can be seen in a warehouse, for example—utilize direct thermal technology.
The main disadvantage of direct thermal printing is its sensitivity to environmental factors. Exposure to heat, light, and other harsh conditions can cause the printed image to darken and become unreadable. This means direct thermal prints are not suitable for long-term use or environments with extreme temperatures or prolonged sunlight.
Direct thermal printers are suitable for printing simple images, such as:
- Shipping labels
- Receipts
- Ticket printing
- Various barcode applications
Besides direct thermal and thermal transfer printing methods, thermal printers come in various models and sizes to suit different applications. Let’s look at some common thermal printer models and sizes.
Thermal Printers Model Options and Sizes
Thermal printers come in various model options and sizes. These variations include differences in print width, resolution, and connectivity options, as well as whether they are designed for portable, desktop, or industrial use.
Thermal Printers Model Options
- Desktop Printers: These are compact and suitable for light to medium-duty printing, often found in retail or office environments.
- Industrial Thermal Printers: Designed for demanding environments and higher print volumes, these thermal printers are often used for barcode and label printing in warehouses or manufacturing facilities.
- Mobile Printers: These thermal printers are portable and lightweight and are used for on-the-go printing, such as in delivery services or field work.
Thermal Printers Size Options
- Receipt Printers: 58mm and 80mm are the most common widths. Some specialized printers may use 76mm or 110mm.
- Label Printers: 2-inch, 3-inch, and 4-inch wide labels are standard.
Apart from the above standard options, thermal printers also come in custom sizes to accommodate diverse needs.
Now that you know how different thermal printers work, their advantages and possible disadvantages, and their uses in various fields, it’s time to determine the best option for your business.
Choosing the Right Thermal Printer For Your Business
- Print Volume and Speed: Determine how many labels, receipts, or other items you need to print per day or hour. High-volume businesses will need faster printers with high-duty cycles.
- Print Quality and Resolution: If you need to print detailed barcodes, logos, or images, a higher resolution (300 dpi or more) is essential.
- Durability and Reliability: For harsh environments or high-demand applications, choose a robust printer with durable components.
- Connectivity: Ensure the printer supports the necessary connection methods, such as USB, Ethernet, Bluetooth, or Wi-Fi.
- Size and Portability: Consider whether you need a compact, portable printer for on-the-go printing or a larger, stationary model.
- Budget: Factor in the initial cost, maintenance, and consumable costs like the labels and ribbons.
- Paper Width and Size: Choose the appropriate paper width and size based on your business requirements.
- Auto-Cutter vs. Manual Tear: Consider whether you need an auto-cutter for faster transaction processing or if a manual tear bar is sufficient.
- Compatibility: Ensure the thermal printer is compatible with your existing software and hardware.
- Maintenance: Factor in the ease of maintenance and the availability of replacement parts.
By carefully assessing these factors, you can select the thermal printer that best fits your business needs and ensures efficient, reliable printing.
For those looking for thermal transfer printers that are easy to use, fast, and have industrial-strength toughness, LabelTac® Printers are the best option. This line of printers was designed to serve the needs of industrial facilities. These thermal transfer printers come with LabelSuite™ software, which makes it easy to design labels to fit any company's needs and to include OSHA-compliant headings and signal words.
Similar Articles
- Beginner’s Guide To Ribbon Printers
- Barcode Labeling
- Asset Tags: Tracking Inventory & Equipment
- Your Guide to Pipe Labeling Standards
- What is QCDSM?
- Labeling Electrical Conduits
- What is a Kaizen Event? [Planning and Execution]
- Creating a Visual Workplace
- 5 Lean Principles for Process Improvement
- ANSI Color Codes for Pipe Marking



