
Completing a Process Hazard Analysis
Process Hazard Analysis, or PHA, is defined as a set of organized and systematic assessments of potential hazards that put employees and equipment at risk within an industrial process. PHAs can be seen being used to determine the causes and consequences of dangerous incidents such as fires, explosions, the release of hazardous chemicals, and other workplace hazards. This type of risk management tool works by focusing efforts on looking at all parts of a process and monitoring those that interact with it, whether that be people or machines.
Completing a process hazard analysis is required by OSHA in 29 CFR 1910.119. Once completed, a PHA must be revalidated every five years thereafter. This is to make sure that no changes are missed, or in the event that one has taken place, an opportunity is able to be taken to thoroughly study it for various hazard prevention efforts.
There are five core concepts that a PHA follows to be able to catch any and all hazards and risks within any kind of manufacturing process. Those in charge of the PHA program must be familiar with the following to be able to instill the proper qualities of this type of management tool:
- Identify problems and hazards
- Evaluate the potential hazards
- Recommend further preventative actions
- Act to address those hazards
- Revalidate the process
To be able to attain those core concepts, OSHA has instilled minimum requirements that must be met within a hazard prevention program such as this. It doesn’t matter what type of PHA is used, as long as the following criteria are met:
- Address the hazards within the process
- Identify previous incidents that had the potential to be disastrous
- Determine engineering and administrative controls that will eliminate or mitigate those hazards
- Identify the consequences if in the event those controls fail
- Address the location of the facility and human factors
- Conduct a qualitative evaluation for possible consequences of process failure
Process hazard analysis is the working foundation for process safety management and risk management programs. In fact, PHA encompasses a wide swath of options for completing those minimum requirements set by OSHA. Some of those options include the following:
- Hazard and Operability Studies (HAZOP)
- What-If Studies
- Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FEMA)
- Major Hazard Analysis (MHA)
- Fault Tree Analysis
PHA can be considered a form of insurance for employers as it helps to protect the company from catastrophic incidents that often come with incredibly high costs for repair and compensation. A PHA also has the ability to eliminate or protect against downtime, property damage, product quality problems, and bad publicity from incidents.
What is HAZOP?
HAZOP, one of the methods that can be used for process safety management, stands for Hazard and Operability Study and is most often described as a qualitative risk assessment tool, a brainstorming approach to risk management, or even as a “bottom-up” risk identification approach. HAZOP is a process by which a new or existing operation, process, policy, or standard is examined to evaluate what types of risks may exist within the environment, operator risk, and equipment/design risk. What makes HAZOP unique is the fact that it’s based on the theory that risks manifest when deviations from the original operational or design intent are present.
When performed properly in businesses such as refining, chemical industries, oil or gas, pharmaceutical, power generation, and other similar places, the identified hazards are sure to be remedied to prevent injuries, fatalities, and damage to equipment. HAZOP can be a valuable tool for employers when thinking about improving workplace safety.
This technique is set up in a way to help not just look at the step-by-step processes, but also the intentions and deviations that occur in operation. HAZOP works by identifying all the possible unintended steps that can take place to expose potential risks. Unlike most traditional hazard identification processes, HAZOP goes even further than just looking at what occurs when everything goes as planned.
Guide Words
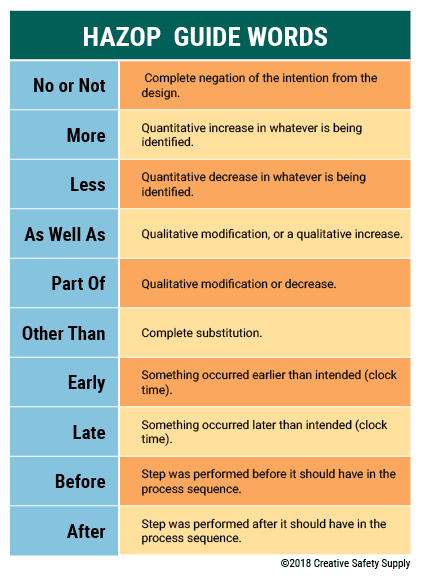
Each guide word has a set meaning when applied to different nodes or variations of the plan. The following is a common set of guide words used in many industries:
- No or Not - The complete negation of the intention from the design
- More - There is a quantitative increase in whatever is being identified
- Less - There is a quantitative decrease in whatever is being identified
- As Well As - There is a qualitative modification, or a qualitative increase
- Part Of - There is a qualitative modification or decrease
- Other Than - There was a complete substitution
- Early - Something occurred earlier than intended (clock time)
- Late - Something occurred later than intended (clock time)
- Before - A step was performed before it should have in the process sequence
- After - A step was performed after it should have in the process sequence
Where Guide Words Are Used
Utilizing guide words is an important step within the four phases of a HAZOP initiative for risk management. They are used to describe almost any type of parameter in a process or procedure. Some common parameters that are looked at include flow, pressure, temperature, level, time, reaction, start-up, shutdown, draining, maintenance, etc.
In fact, utilizing guide words is one of HAZOP’s defining features since they aim to pick apart every single process and the potential outcomes if something goes wrong. Other continuous improvement and risk assessment programs find a problem and fix them right there rather than predicting issues like HAZOP does.
When should a HAZOP be done?
A HAZOP study, just like any other hazard management program, should be completed in phases within a risk management project. Ideally a HAZOP assessment begins when there is a new process or a process that has changed in the working environment. This can be anything from a new machine being added to a change made to simplify work. To do so, the method relies heavily on the following four phases:
- Define: This stage requires the risk assessment team to discuss relevant ideas to ultimately focus their efforts.
- Define the scope, objectives, responsibilities, and select the team
- Prepare: This stage often includes the usage of guide words to help identify key issues within a process.
- Plan the study
- Collect all necessary data
- Choose a style of documentation
- Arrange and schedule time and activities
- Exam: The chosen guide words are applied to the examination phase as they play a role in thoroughly searching for deviations in the process. It also must be noted that all reasonable use and misuse conditions found within the process must be challenged to the point of determining if they are credible.
- Divide the system in question into parts and identify potential areas of deviation from intent by utilizing guide words
- Point out consequences and causes of specific recognized issues
- Identify if those issues are significant
- Put together measures or mechanisms that protect and detect problems
- Identify mitigation measures
- Document: Templates are often used for this type of documentation. One of such can be found in the IEC 61882 Standard.
- Record examination and sign off on the documentation
- Produce a report of the risk management measures
- Follow up on the changes made and re-study those changes if needed
- Produce the final report
Assembling a Team
Operability of this method requires a team of experts in areas such as operations, maintenance, instrumentation, engineering, process design, etc. The ideal team size entirely depends on the process or procedure being evaluated but should be kept as small as possible without sacrificing necessary talent or knowledge. The most common roles for this team are:
- Study Leader - This person leads the study and should have experience with HAZOP studies already.
- Recorder / Scribe - This person documents everything about the study including causes, consequences, actions, deviations, and more.
- Process Designer - This person provides details about the intent of designs.
- Operator - This person will operate the process.
- Specialist - This person provides specialized technological knowledge about the process.
- Maintainer - This person offers information and details about the maintenance of equipment or other machinery.
Advantages and Disadvantages to Using HAZOP
HAZOP is an invaluable tool when it comes to hazard analysis. In fact, there are several advantages that it holds unique to itself. The first one is its helpfulness when facing hazards that are difficult to measure, such as ones rooted in human behaviors and ones that are difficult to detect. The reason being because HAZOP doesn’t directly ask the risk management team to measure this kind of deviation from what is normal. Instead, they are required to use guide words that give them the ability to predict hazards before they occur.
HAZOP also has a built-in brainstorming method that helps with those hazard predictions. It relies on this aspect heavily. Lastly, HAZOP is a systematic and comprehensive method that is much simpler to use than other traditional risk assessment methods.
As for disadvantages, HAZOP does not have the ability to assess hazards regarding the interaction of different processes within systems. There is also no prioritization strategy that comes with this method. And lasty, there is no way that the users can assess the effectiveness of new or already existing controls.
With all that in mind, HAZOP is only one of the numerous methods that a company can use to find and solve hazardous situations within the workplace. It is also good to keep in mind that many of these types of methods can be used in tandem with each other to provide a more overreaching hand in keeping employees, equipment, and quality of product safe and efficient.
Similar Articles
- Job Hazard Analysis: Addressing Coronavirus Risk in Your Workplace
- Fault Tree Analysis
- Bottleneck Analysis
- Job Safety Analysis
- The Five Whys (Root Cause Analysis)
- What is HAZCOM? (Hazard Communication Definition + OSHA Standards)
- Understanding Risk Assessments in the Workplace
- Value Stream Mapping (VSM Analysis)
- Kano Model (Analysis & Diagram)

